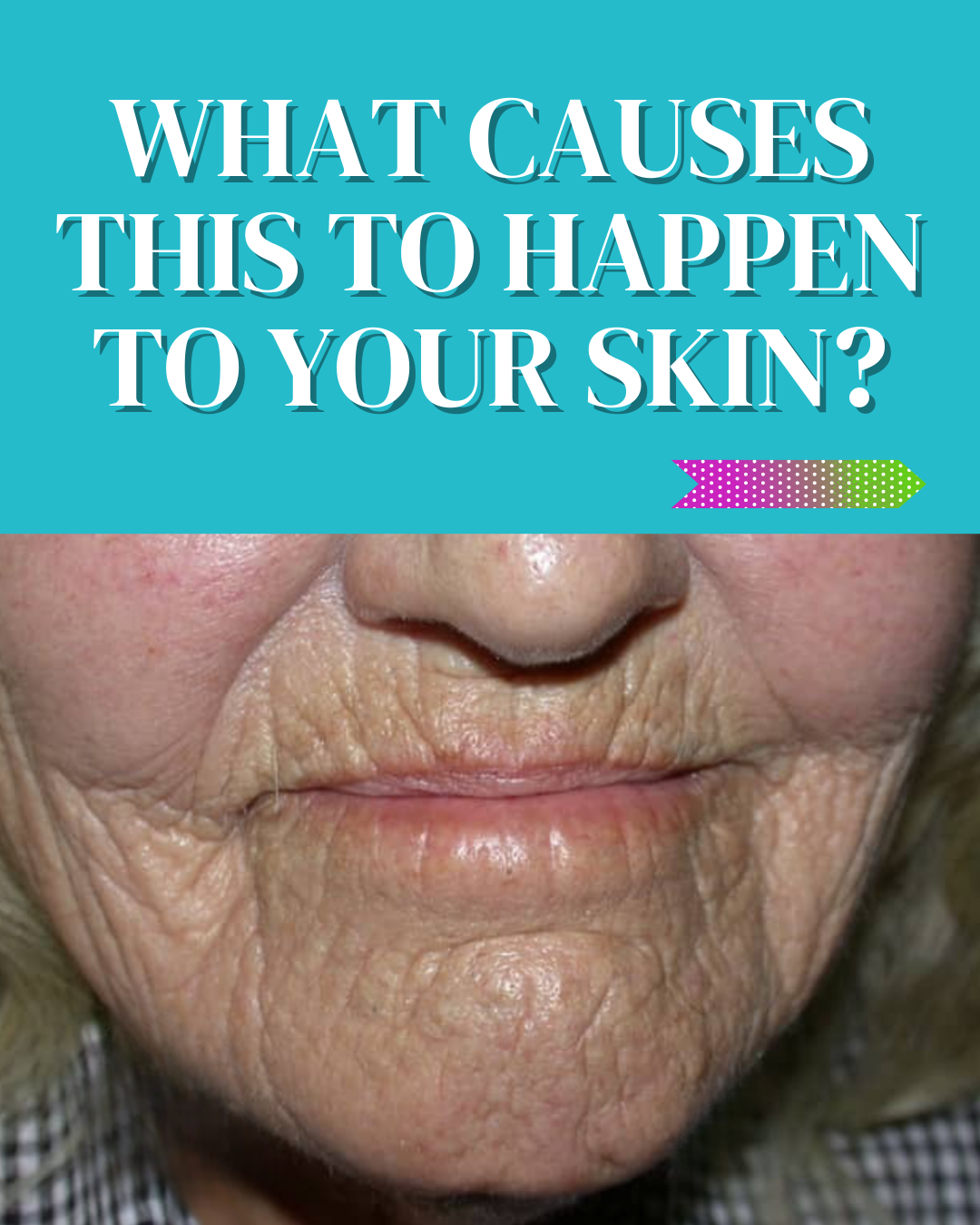
Sugar Consumption is at the top of the list of things that cause premature aging.
Sugar causes Glycation leading to deep wrinkling of the skin.
When there is too much sugar in the body, glucose and fructose molecules attach themselves to collagen and elastin proteins in the skin creating AGE’S (advanced glycation end products) these make collagen rigid over time leading to damaged skin.
Collagen plays a vital role in youthful-looking skin by acting as a scaffolding structure that provides the internal support structure necessary for smooth, plump skin.
Glycation accumulates with a rate of about 3.7% per year reaching a 30-50% increase by age 80. The visible signs of glycation can be seen as early as the age of 30, when the body becomes less resilient and produces less collagen.
What are advanced glycation end products? AGEs degrade collagen integrity compromises its ability to self-repair, inhibiting its removal and replacement by new collagen leaving you with weak and brittle collagen.
AGEs are formed intracellularly and extracellularly. Many intracellular components can be affected by glycation with detrimental effects on their function including cytoskeleton proteins, enzymes, DNA and lipids. Cytoskeletal proteins are important in providing stability for the cytoskeleton and are crucially involved in numerous cellular functions such as migration and cellular division. Intracellular glycation in the skin adversely affects keratinocyte and fibroblast function which are crucial parts of youthful skin.
AGEs can be formed directly in the body or be exogenously ingested by eating broiled, fried or barbecued food. Reactive oxygen species (ROSs) accelerate AGE formation. For healthy people with normal blood glucose levels, glycation happens gradually and slowly over a lifetime. Diet and lifestyle choices can affect glycation. In fact, yellowing of skin often seen prematurely in smokers is a sign of glycation. Smoking reduces antioxidants in the skin so there is little antioxidant reserve to slow glycation. AGE formation is increased with age, smoking, poor diet and possibly UV exposure
AGEs not only exert their deleterious actions directly but also indirectly through their interaction with specific cell surface receptors called receptor for AGEs (RAGE).
When AGEs bind to RAGE, it initiates a cascade of signals negatively influencing cell cycle and proliferation, gene expression, inflammation and ECM protein synthesis. Keratinocytes, fibroblasts, dendritic cells and to a less extent endothelial cells and lymphocytes express RAGE. RAGE activation can directly induce oxidative stress and inflammation.
So how do we prevent glycation and AGE formation?
Since oxidation steps are involved in the formation of many AGEs, antioxidants may have antiglycation abilities. In addition to maintaining a healthy diet, low in simple sugars and high in antioxidants, there are now skin care ingredients that specifically target glycation and AGEs. Your esthetician can give you advice on which products are best for you.
What can you do immediately to help?
Since SUGAR is the leading cause of glycation you may also use Intermittent fasting as a method to control your excess sugars from being retained in cells.
Intermittent fasting doesn’t mean skipping meals, it means time restricted eating.
Start Slow – an easy way to do this is by only eating for a time span of 12 hrs. per day and fasting the other 12 hrs.
You can consume nothing but hydration in the form of water or tea, no calories, carbs, fats or protein in the fasting window.
A more advanced level of intermediate fasting will get you to Autophagy even faster. This is eating for only the most active 6 hrs. of your day and fasting the other 18 hrs. of your day.